
Dorsal body cavity Wikipedia Human anatomy and physiology, Anatomy
Cavities Diagram. 1 The human body is divided into a number of body cavities. A body cavity is a fluid-filled space in the body that holds and protects internal organs.. 2 The ventral cavity is at the anterior, or front, of the trunk.. 3 The dorsal cavity is at the posterior, or back, of the body, and includes the head and the back of the.
PPT The Human Body Anatomical Regions, Directions, and Body Cavities
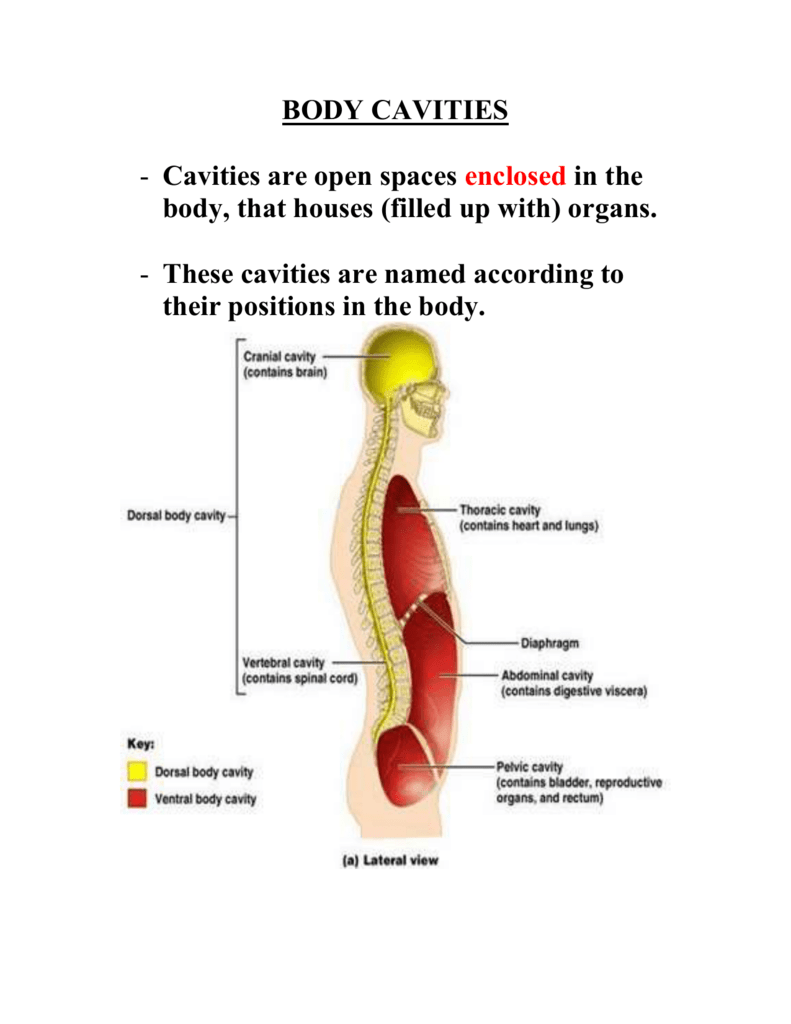
Cavities: Because things need to be kept somewhere. A concept easier to grasp than planes and directional is body cavities, as they are a physical thing. When you hear the word "cavity," no doubt you think of the kind in your teeth that are caused by plaque. A cavity, in any capacity, is a hollow place.
body cavities Winston Knoll Collegiate
There are four paired sinuses (named for the skull bones in which they are located) in the human head: Frontal sinuses: The right and left frontal sinuses are located near the center of the.
PPT Body Cavities PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2759699
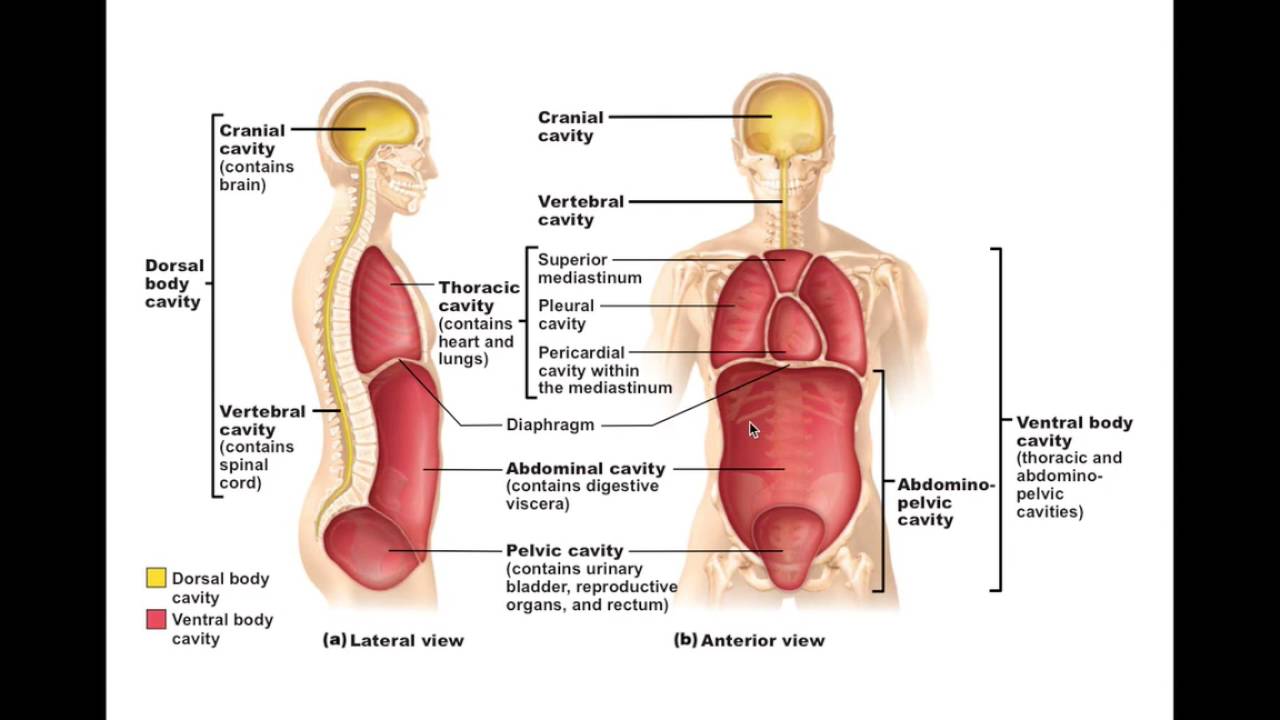
A body cavity is any space or compartment, or potential space, in an animal body. Cavities accommodate organs and other structures; cavities as potential spaces contain fluid. The two largest human body cavities are the ventral body cavity, and the dorsal body cavity. In the dorsal body cavity the brain and spinal cord are located.

Body Cavities Chest Cavity Anatomy and Body Cavities Anatomy
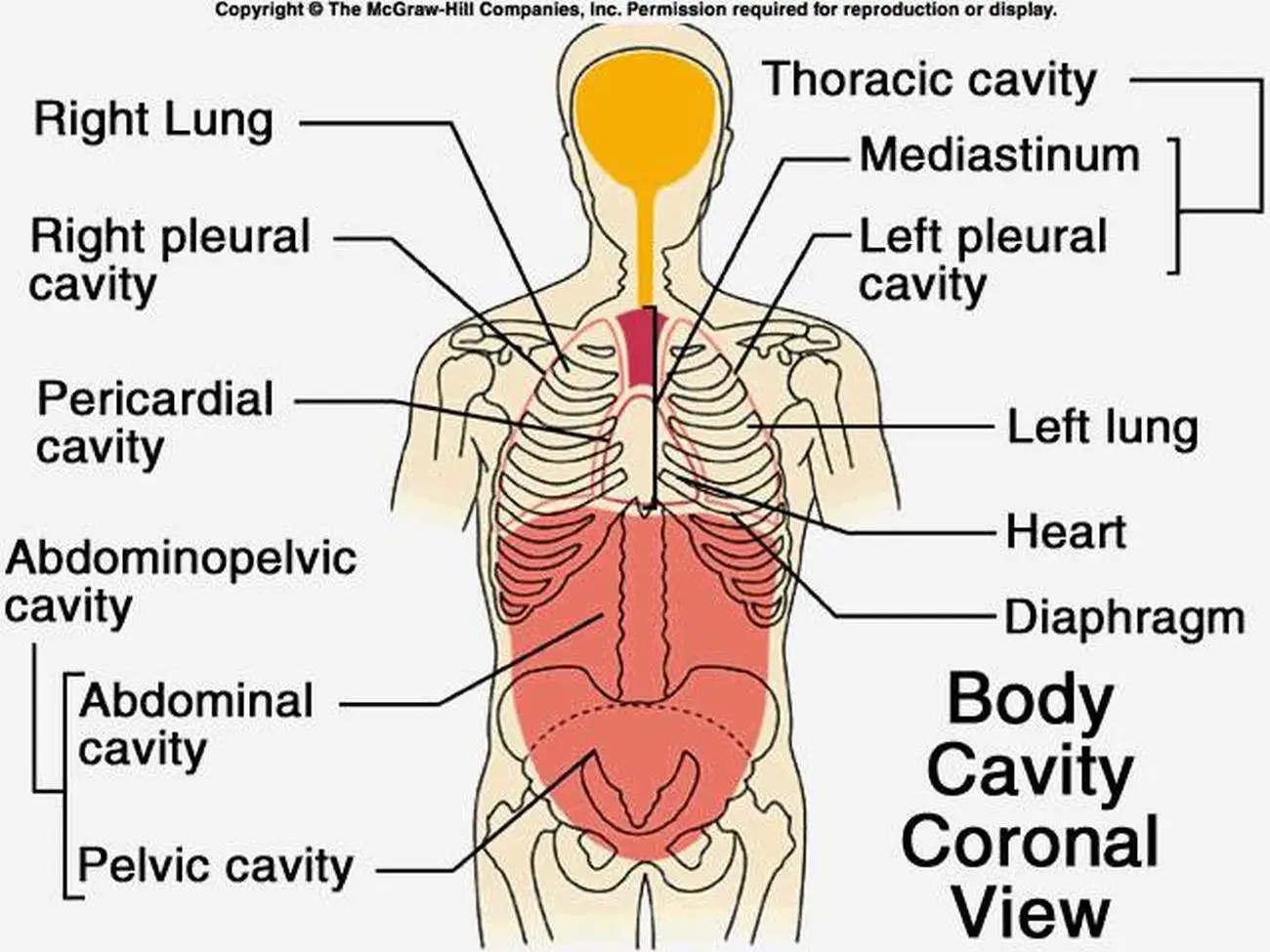
What body are cavities located superior to the diaphragm? The cavity that locates superior to the diagram is the thoracic cavity. Some important organs like the heart, lung, parts of the aorta, cranial and caudal vena cava are present within this thoracic body cavity of an animal. What are the major body cavities and their organs?
Solved Body Cavity Diagram Instructions Fill in the body
Abdominal Body Cavity: Labeled diagram of the abdominal cavity showing the small intestine (brown) covered by the visceral peritoneum (inner green layer), and the parietal peritoneum (outer red layer) lining the abdominal cavity. The peritoneal cavity is the potential space between the visceral and parietal peritoneum and contains peritoneal fluid.
Cavities of body and anatomical compartment medical division outline
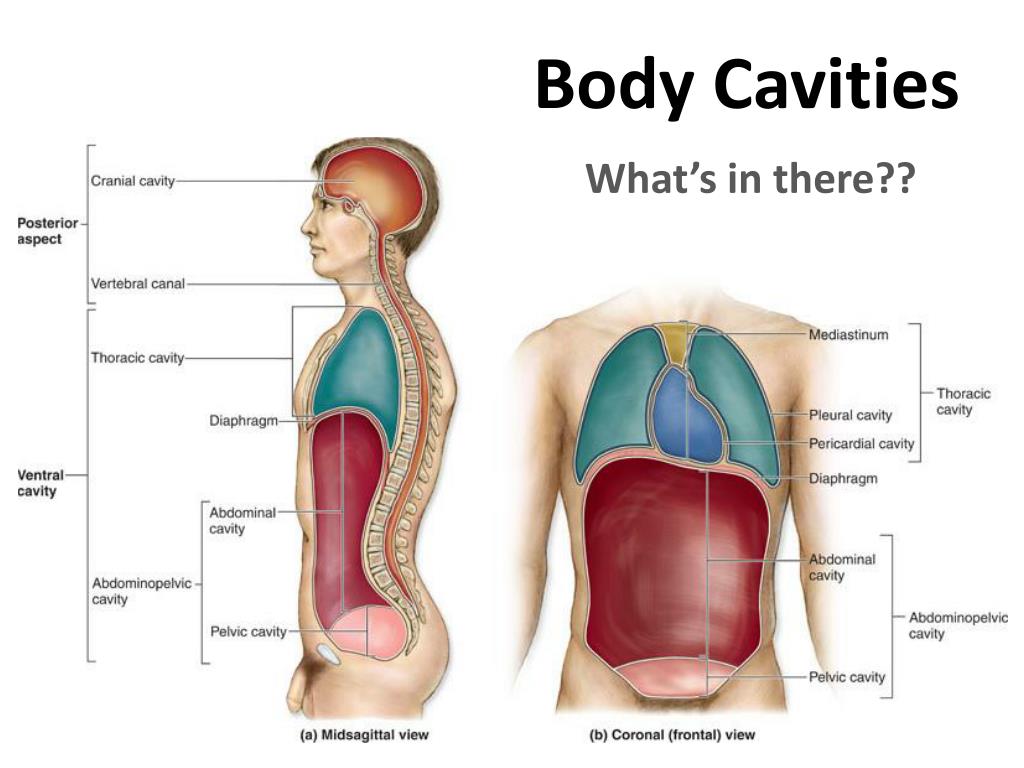
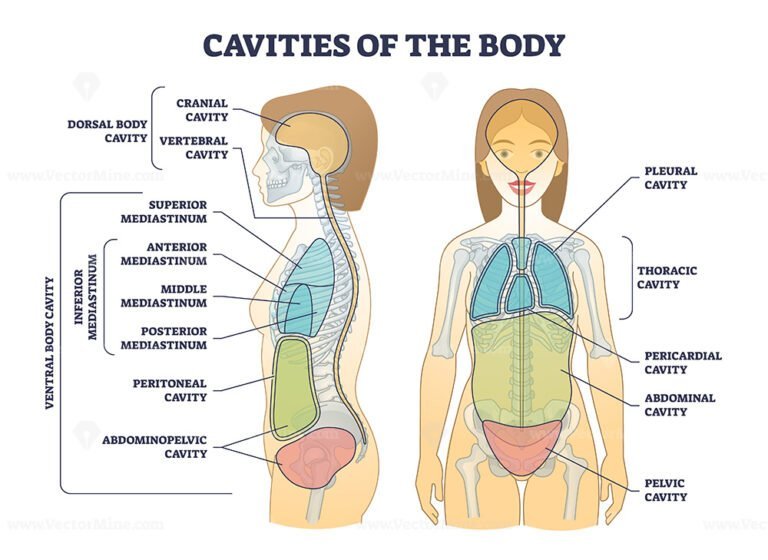
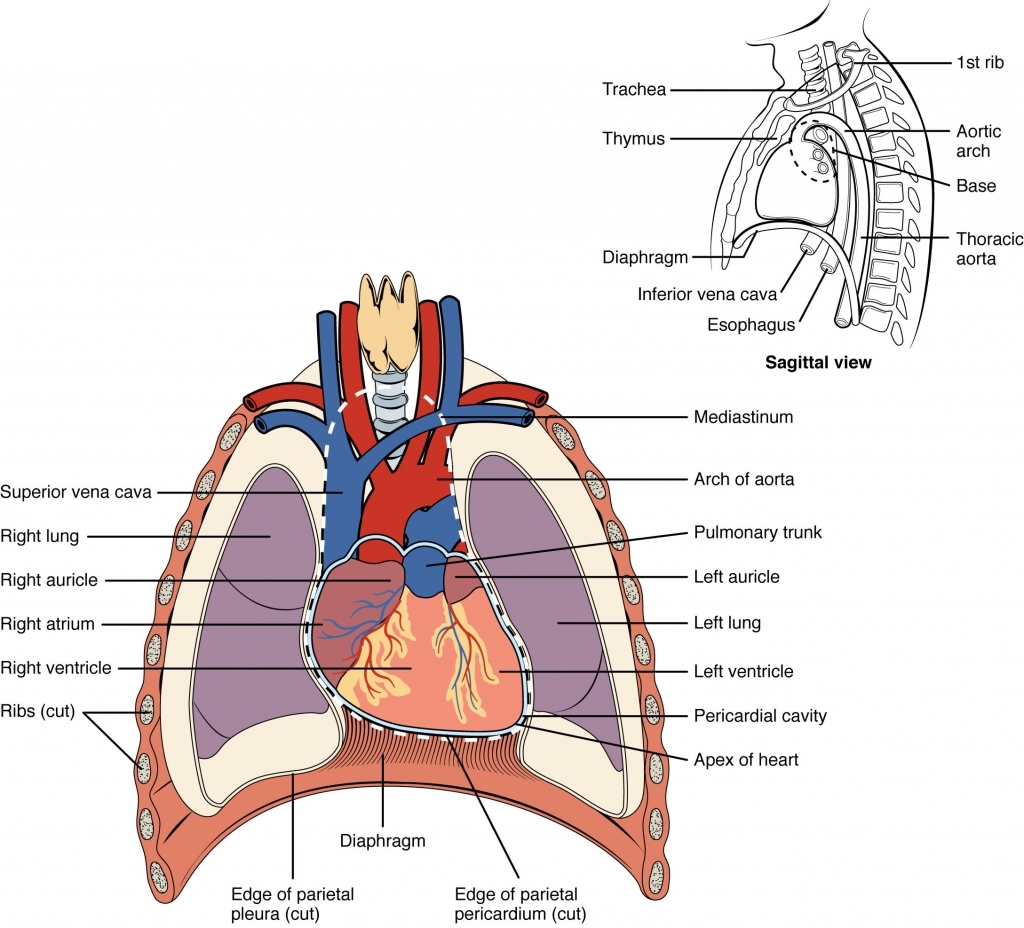
Information. The major cavities of the human body are the spaces left over when internal organs are removed. There are additional body cavities which we will only discuss in lecture. These are the cavities created by serous membranes-the pleural cavities, the pericardial cavity, and the peritoneal cavity-and the mediastinum.
Major Cavities Of The Body cloudshareinfo
Body Cavities and Serous Membranes. The body maintains its internal organization by means of membranes, sheaths, and other structures that separate compartments. The dorsal (posterior) cavity and the ventral (anterior) cavity are the largest body compartments (Figure 1.15). These cavities contain and protect delicate internal organs, and the.
Anatomical Terminology Learnful
The thoracic cavity is the anterior ventral body cavity found within the rib cage in the torso. It houses the primary organs of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, such as the heart and lungs, but also includes organs from other systems, such as the esophagus and the thymus gland. The thoracic cavity is lined by two types of mesothelium.
Pictures Of Cavity, Anatomical
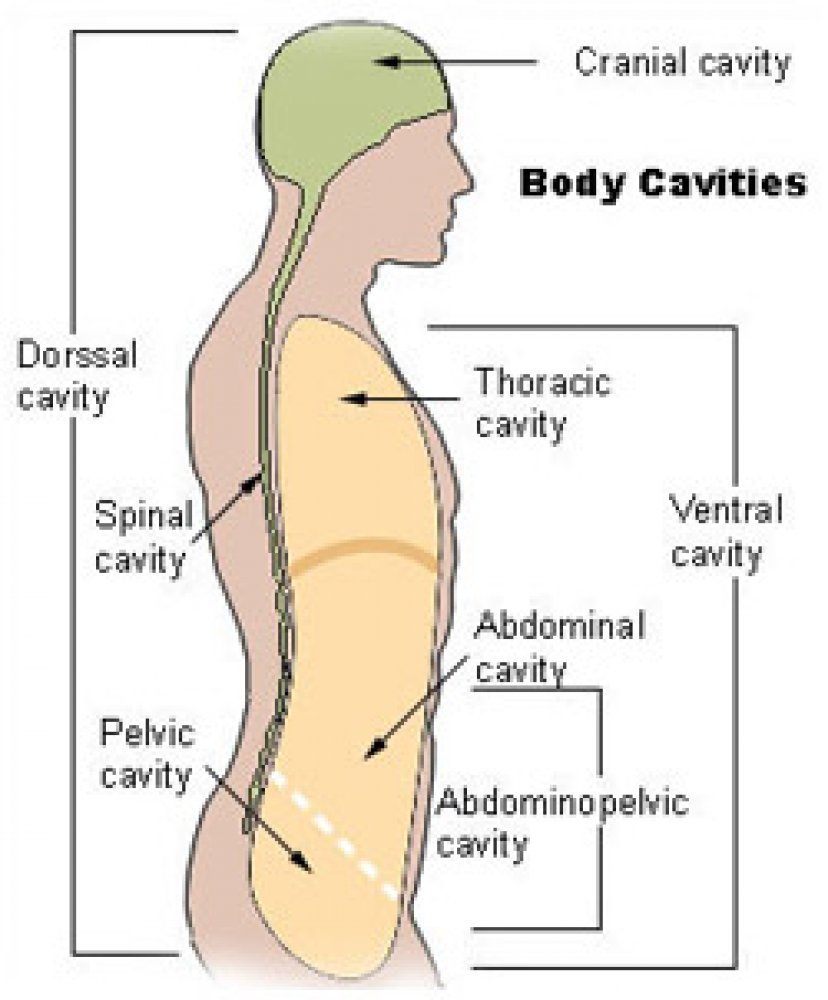
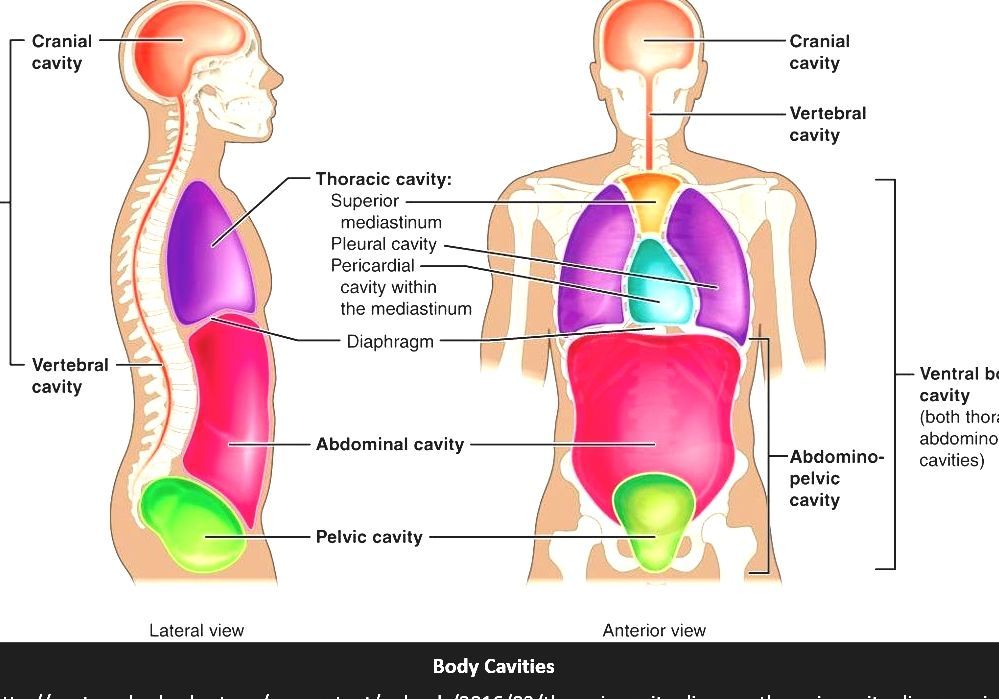
Figure 33.6.1 33.6. 1: Body cavities: Vertebrate animals have two major body cavities. The dorsal cavity, indicated in green, contains the cranial and the spinal cavity. The ventral cavity, indicated in yellow, contains the thoracic cavity and the abdominopelvic cavity. The thoracic cavity is separated from the abdominopelvic cavity by the.
Organization of the Body
Summary. The five vital organs in the human body are the brain, heart, lungs, kidneys, and liver. Other organs include the gallbladder, pancreas, and stomach. Organ systems, such as the nervous.

Intro to Anatomy 1 Life, Organization, and Terminology Freethought Forum
Figure 1.4.3 - Planes of the Body: The three planes most commonly used in anatomical and medical imaging are the sagittal, frontal (or coronal), and transverse planes. Body Cavities . The body maintains its internal organization by means of membranes, sheaths, and other structures that separate compartments.

Dorsal Body Cavity Diagram Diagram Media
A body cavity is a space created in an organism which houses organs. It is lined with a layer of cells and is filled with fluid, to protect the organs from damage as the organism moves around. Body cavities form during development, as solid masses of tissue fold inward on themselves, creating pockets in which the organs develop.
Body Cavity Diagram ClipArt Best
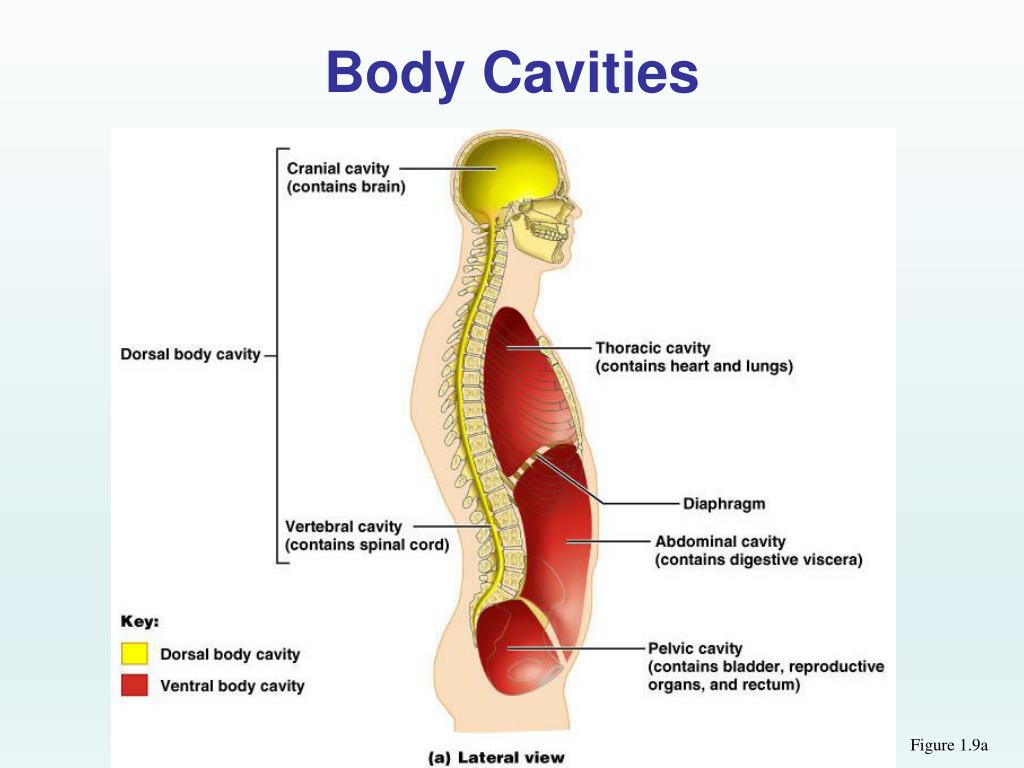
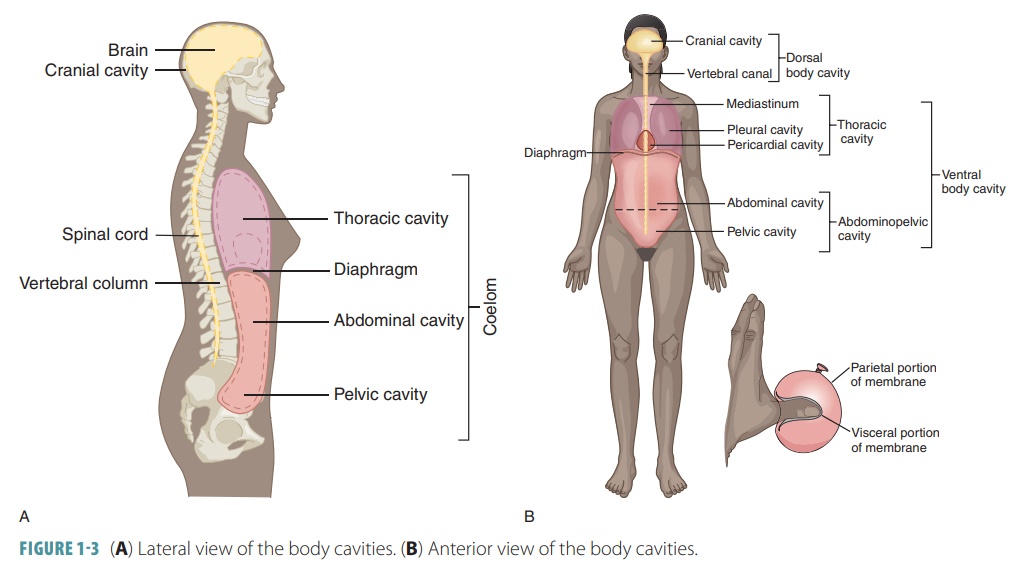
The dorsal cavity is at the posterior, or back, of the body, including both the head and the back of the trunk. The dorsal cavity is subdivided into the cranial and spinal cavities. The cranial cavity fills most of the upper part of the skull and contains the brain. The spinal cavity is a very long, narrow cavity inside the vertebral column.

Major Cavities Of The Body cloudshareinfo
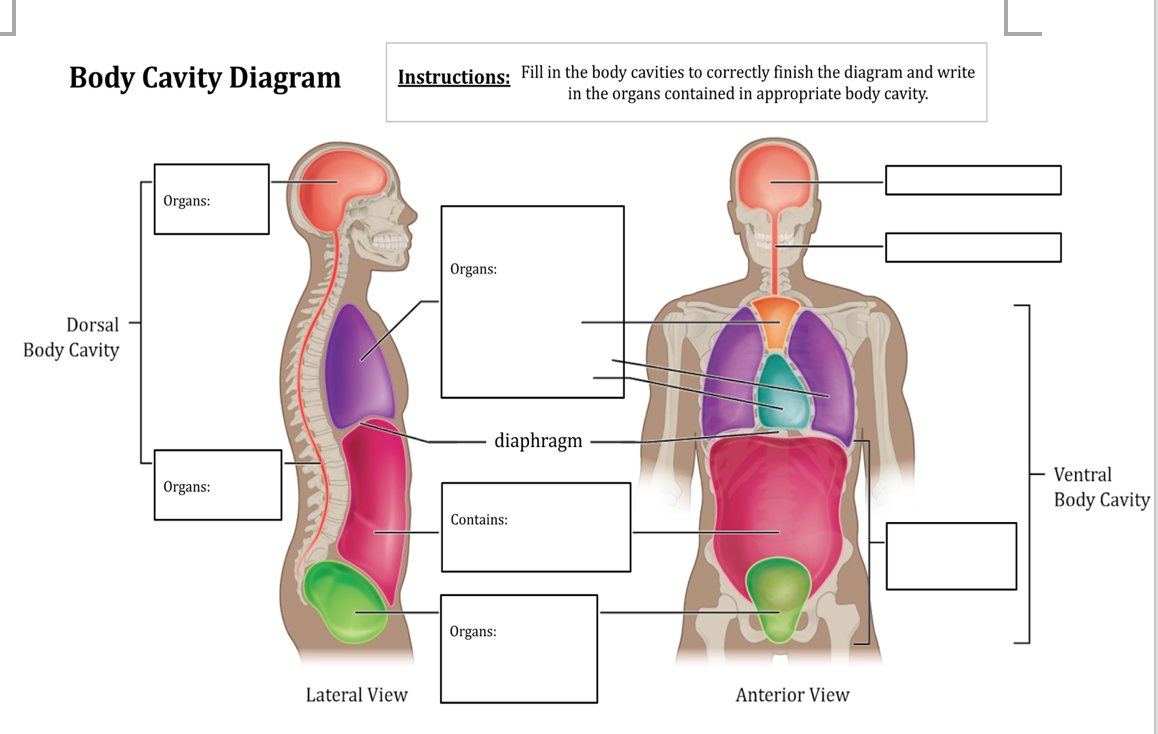
Schematic diagrams of the bodies of animals with coeloms, with pseudocoeloms, or without body cavities. functions of body cavities. Humans have four body cavities: (1) the dorsal body cavity that encloses the brain and spinal cord; (2) the thoracic cavity that encloses the heart and lungs; (3) the abdominal cavity that encloses most of the.
Body Cavity Cavities Of The Human Body
The cranial cavity is a large, bean-shaped cavity filling most of the upper skull where the brain is located. The vertebral cavity is a very narrow, thread-like cavity running from the cranial cavity down the entire length of the spinal cord. Together the cranial cavity and vertebral cavity can be referred to as the dorsal body cavity.